How to Protect SEO Performance During a Site Migration
Arming yourself with the right tools to ensure a smooth site migration is important - find out how to protect your SEO during a migration today.
Read moreURL parameters can cause several issues for a website such as duplicate content and keyword cannibalisation. Tom Williams provides his top tips to help you avoid these issues on your website.
URL parameters are the parts within the address of a web page that are present after a question mark, sometimes referred to as query strings or query string parameters.
The following URLs all point to the same content, a collection of ‘Rugs’:
http://www.example.com/category/home-and-furniture/home-furnishings/rugs
http://www.example.com/category/home-and-furniture/home-furnishings/rugs?colour=red
http://www.example.com/home-and-furniture/home-furnishings/rugs?colour=red&style=plain
These types of URL parameters are common on e-commerce websites that use faceted navigation systems. This allows users to browse products by using a selection of filters.
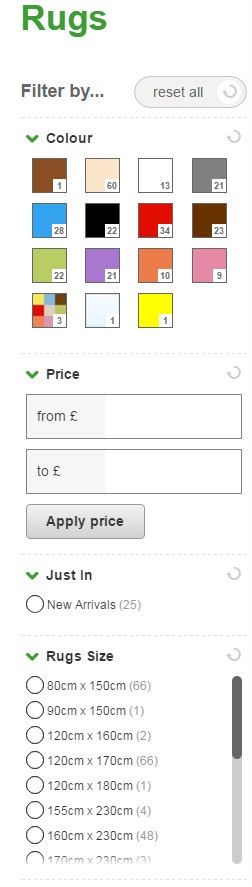
Using a faceted navigation system can result in the creation of many URLs all serving very similar content. While this can be beneficial for users, it can give search engines a headache and may affect your SEO visibility.
Google refers to two different two types of parameters - active and passive.
Active Parameters
Active parameters can change the content on a web page. A few examples can be found below:
Passive Parameters
Passive parameters don’t change the content on a web page. These parameters are commonly used to track visits and referrers but don’t have any effect on the page.
The two URLs below point to the same content:
The second example provides information on where the user came to the site from, in this case Google Maps. These are commonly used for tracking clicks in inbound marketing campaigns, such as emails and newsletters.
Duplicate Content
URL parameters can cause duplicate content. Let’s imagine there’s a block of content on the main ‘Rugs’ category page of a website - http://www.example.com/category/home-and-furniture/home-furnishings/rugs.
When a filter is applied to show ‘Red’ rugs http://www.example.com/category/home-and-furniture/home-furnishings/rugs?colour=red the block of content stays the same.
If the relationship isn’t made clear by the webmaster then this could be seen as duplicate content.
We will explain how to overcome this further on in our post.
Keyword Cannibalisation
Keyword cannibalisation occurs when several pages on a website target the same keywords. This causes problems for search engines when they’re deciding which page to rank for the relevant keyword. The end result could mean that a less relevant page is ranked higher than one with more relevant content, simply because they mention the same keywords but in a higher volume.
A good example of this is present on www.booking.com. For the search term ‘Hotels in Dubai’, booking.com has two results in the SERPs:
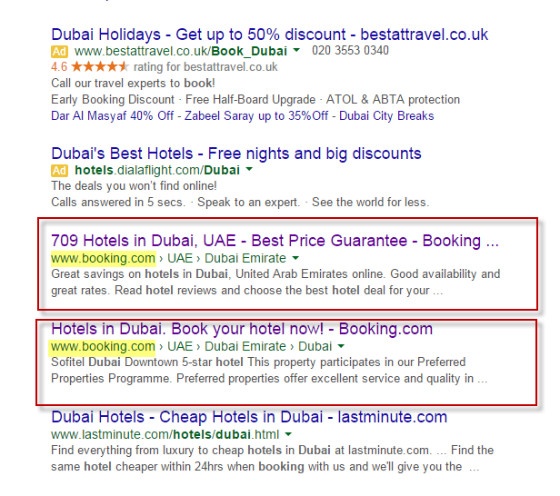
http://www.booking.com/city/ae/dubai.en-gb.html
http://www.booking.com/searchresults.en-gb.html?city=-782831
While these two pages aren’t identical and may not been seen as duplicate, it doesn’t mean they won’t cause problems.
Having two pages on the website that include the phrase ‘Hotels in Dubai’ can hold back the performance of both pages as this will confuse search engines, meaning they will be unsure of which page to rank.
There are two questions that will help a webmaster understand whether URL parameters are causing an issue on their website:
If the answer to either of these questions is yes, URL parameters may be causing your website issues.
However, if the content on your website changes when a filter is selected, then URL parameters are not an issue.
For example, if the title, description, <h> tags, on page content etc. on the following page (http://www.example.com/category/home-and-furniture/home-furnishings/rugs?colour=red) is tailored to ‘Red Rugs’ rather than being a copy of the main ‘Rugs’ category page, this would not be considered an issue.
Let’s now take a look at how issues caused by URL parameters can be addressed.
Canonical tags are used to indicate to search engines the preferred URL of a web page.
Let’s consider the following URLs:
http://www.example.com/category/home-and-furniture/home-furnishings/rugs?colour=red
http://www.example.com/home-and-furniture/home-furnishings/rugs?colour=red&style=plain
Both should have a canonical tag pointing to the main category page:
http://www.example.com/category/home-and-furniture/home-furnishings/rugs
This means that search engines should rank the main category page over the pages with URL parameters within them.
There is a feature in Google’s Search Console that allows webmasters to indicate how Google should handle parameters in their URLs - https://www.google.com/webmasters/tools/crawl-url-parameters.
More information on how to use this tool correctly can be found here - https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/6080550?hl=en.
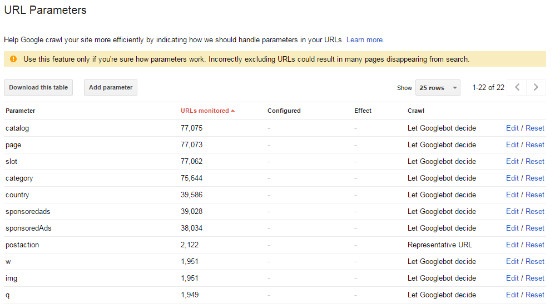
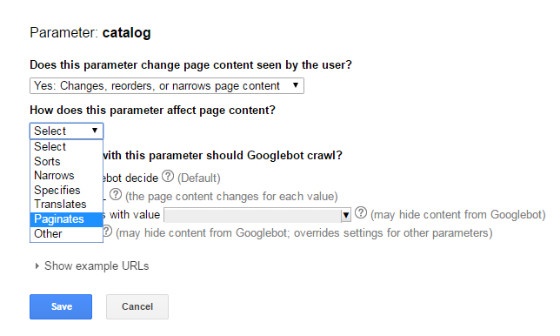
The robots.txt file can be used to block search query parameters from being crawled by search engines. However, this won’t stop search engines from indexing these pages.
The following line can be added to the robots.txt file to achieve this:
Disallow: /*?*
You need to ensure there aren’t any other pages on your website that have a question mark within the URL that you don’t want blocked.
To conclude, URL parameters can cause several issues if not used correctly. If the content on your website changes when filters are selected, there’s no reason to worry.
If the content on your website is identical or very similar when filters are selected, the three methods to avoid being penalised are - applying canonical tags, using the URL Parameters tool or using the robots.txt file.
Not sure if URL parameters are causing issues for your website? Contact our technical SEO team today.
Find out more about our technical SEO services on our SEO Consultancy page.
More articles you might be interested in:
Arming yourself with the right tools to ensure a smooth site migration is important - find out how to protect your SEO during a migration today.
Read more
Google employees have recently announced that the upcoming Google Core Update is set to be released in the coming weeks. Understanding and addressing...
Read more
Language matters. Any marketer worth their salt knows this. But when discussing gender and sexual orientation, that importance is amplified tenfold.
Read more
When marketers think of thought leadership, there are names rather than ideas, that tend to spring to mind.
Read more
With the release of GPT-4, how revolutionary will this tool be? Alan Rowe takes us through it...
Read more
To help prompt you to consider your approach to organic search integration, Dr. Dave Chaffey gives some practical tests you can apply to review your...
Read more
Learn more about the importance of understanding the user journey to create a content strategy that is on point.
Read more
Google's change in guidance could transform the way content is created in the future, but how does it affect SEO and content creators going forward?
Read more